网络流基本概念
网络:一张有向图 ,其上的边的边权叫做容量。额外地,它拥有一个源点和汇点。
流:如果把网络想象成一个自来水管道网络,那流就是其中流动的水,每条边上的流都不能超过它的容量。并且,对于除了源点和汇点外的所有点,流入的流量都等于流出的流量。网络流中最常见的问题就是最大流。假定从源点流出的流量足够多,求能够流入汇点的最大流量。有点像木桶原理,某条路径的容量是由最窄的一根水管决定的。
割:从网络中选择一些边,使得去掉这些边后,剩下两个不连通的分别包含源点和汇点的点集。割的大小是这些边的容量之和。在所有可行的割中,最小的割称为最小割。
Ford-Fulkerson 算法
FF 算法的核心是找增广路。
残余容量:我们找到一条从源点到汇点,流量大于 0
的路径,然后扣除路径上各边相应的容量,这时的容量称为残余容量。
增广路:从源点到汇点的路径,其上所有边的残余容量均大于 0。
Ford-Fulkerson
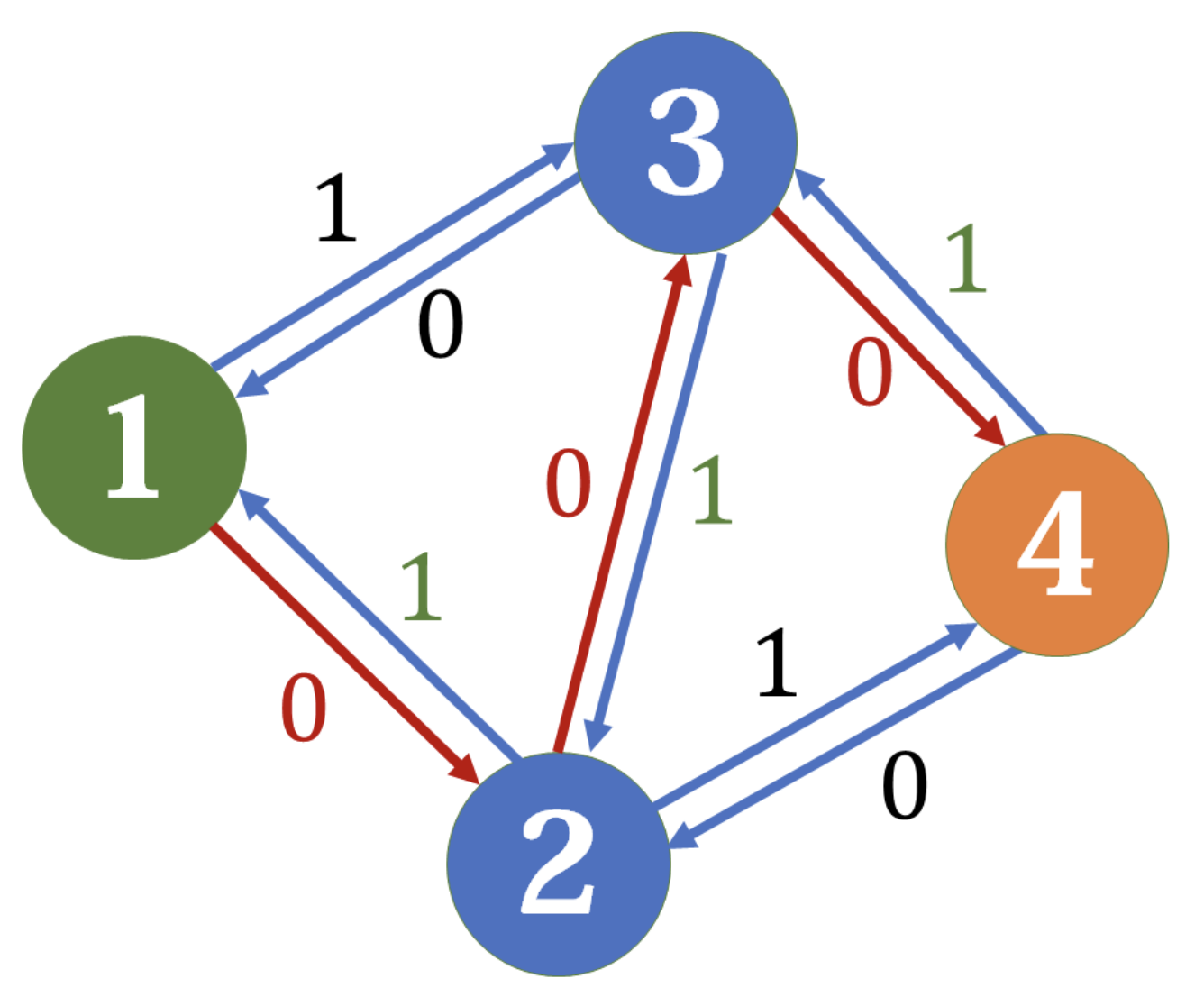
算法就是不断寻找增广路的过程,但是不断找增广路的过程不一定是正确的,例如:
在上图中,如果我们先找到了 \(1\rightarrow
2\rightarrow 3\rightarrow 4\)
的增广路,此时就不能找到别的了,我们求出的最大流会是
1。而实际上的最大流是 2,通过\(1\rightarrow
3\rightarrow4\) 和 \(1\rightarrow
2\rightarrow 4\) 得到。
为了解决这个问题,我们引入反向边。在建边的同时,在反方向建一条边权为
0
的边。在我们寻找到增广路后,在扣除正向边的容量时,反向边加上等量的容量。
image-20250916130543285
这样,我们除了找到 \(1\rightarrow
2\rightarrow3\rightarrow4\) 外,还能找到 \(1\rightarrow3\rightarrow2\rightarrow4\) 。此时我们实际选择了
\(2\rightarrow3\) 和 \(3\rightarrow2\)
两条边,我们可以认为这两条边上的水流抵消了,实际上选择的路径就是 \(1\rightarrow3\rightarrow4\) 和 \(1\rightarrow2\rightarrow4\) 。
可以把反向边理解成一种撤销 ,走反向边就意味着撤回上次流经正向边的若干流量,这也合理解释了为什么扣除正向边容量时要给反向边加上相应的容量:反向边的容量意味着可以撤回的量。
因此,在加入了反向边这种反悔机制后,我们就可以保证当找不到增广路的时候,流到汇点的容量就是最大流。
在这种情况下,如果我们采用 DFS 暴力找增广路,时间复杂度是 \(O(EF)\) ,其中 \(F\) 表示最大流。
Edmond-Karp 算法
EK 算法实际上就是用 BFS 实现 FF 算法,时间复杂度是 \(O(NE^2)\)
Dinic 算法
Dinic 算法是最常用的网络流算法。它是 EK 的优化,先用 BFS 分层,再用
DFS 寻找,复杂度上界是 \(O(NE^2)\) 。分层就是预处理出源点到每个点的距离(每次循环都要预处理一次,因为有些边可能容量变为
0
而不能再走)。我们只往层数高的地方增广,可以保证不走回头路也不绕圈子。
此外,还可以使用多路增广:在某点 DFS
找到一条增广路后,如果还剩下多余的流量未用,继续在该点 DFS
尝试找到更多增广路。
此外还有当前弧优化:在 Dinic
算法中,一条边增广一次就不会再次增广了,所以下次增广时不需要再考虑这条边。我们可以不断更新出边的起点。
这里注意,如果容量均为 1 的话,时间复杂度是 \(O(E\sqrt{N})\) ,可以以更低的复杂度解决二分图匹配问题。
一般来说,\(O(NE^2)\)
也是一个很松的上界,不常用。在很多稀疏图下,常用的复杂度是 \(O(E\sqrt{N})\)
最大流最小割定理
最大流 = 最小割。
费用流
对于每条边,除了容量以外还存在费用 \(c\) ,当一条边的流量为 \(f\) 时,需要花费 \(f\times c\)
的费用。我们将网络中总花费最小的最大流称为最小费用最大流。
做法是考虑贪心,其实就是在最大流的基础上求费用最小,我们在找增广路的过程中先保证它是流过每单位流量费用最小的增广路。这里可以使用
Dijkstra 实现,不过需要注意的是不能出现负的边权,否则要用
SPFA。如果非要用
Dijkstra,需要用到原始对偶优化,首先用最短路算法求出源点到每个点的最短距离
\(h_i\) 作为一个点的初始势能,把从
\(u\) 到 \(v\) 的单位费用为 \(w_i\) 的边权设置为 \(w_i + h_u -
h_v\) ,每次增广后重新将每个点的势能更新并计算新的边权,势能 \(h_i\) 更新为 \(h_i + d_i\) 。
需要知道时间复杂度:\(O(FE\log
N)\) ,其中 \(F\)
是最大流。一般来说网络流算法的数据很难跑满,可以大胆尝试。
题意
给定网络,求起点到终点的最大流。
题解
最大流模版,注意下面写法的注意事项:
采用 Dinic 算法,每轮增广先 BFS,再
DFS。由于需要处理反边,我们对一条边的正反连续编号,邻接表中存边的编号。就能通过与
1 异或的操作快速访问反边。DFS 时引用访问边的编号就能避免多次访问。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, m, s, t; cin >> n >> m >> s >> t; MaxFlow<int > mf (n) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { int u, v, w; cin >> u >> v >> w; mf.addEdge (u, v, w); } cout << mf.flow (s, t) << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
给定网络,求最小费用最大流。
题解
Dijkstra + Primal-Dual 原始对偶算法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, m, s, t; cin >> n >> m >> s >> t; MinCostFlow<int > mf (n) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { int u, v, w, c; cin >> u >> v >> w >> c; mf.addEdge (u, v, w, c); } auto [flow, cost] = mf.flow (s, t); cout << flow << " " << cost << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
网络流建模
网络流的主要难点不是算法而是建模,很多题几乎想不到网络流模型,下面以经典的网络流
24 题为例学习网络流的建模与应用。
link:网络流
24题
题意
\(m\) 个不同单位,第 \(i\) 个单位有 \(r_i\) 人,还有 \(n\) 张桌子,第 \(i\) 张桌子可以坐 \(c_i\)
人。如果要让每张桌子坐的人都是来自不同单位的,给出一个符合条件的方案。
\(m\le 150,n\le 270,r_i,c_i\le
10^3\) 。
题解
可以建立起一个桌子和单位的二分图模型,将每个单位向所有桌子都连一条容量为
1 的边,另外规定一个起点 \(s\) 和终点
\(t\) ,将 \(s\) 与单位连容量为 \(r_i\) 的边,将桌子与 \(t\) 连容量为 \(c_i\) 的边,跑一次最大流即可。
如果存在方案,需要最大流等于所有人数之和。对于输出方案,我们可以遍历每一条边,找出流量为
1,且起点为单位的边,代表该单位有人坐到终点对应的桌子。
时间复杂度:\(O(nm\sqrt{n+m})\) 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, m; cin >> m >> n; int s = n + m + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MaxFlow<int > mf (t) ; int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (s, i, w); sum += w; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (i + m, t, w); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { mf.addEdge (i, j + m, 1 ); } } auto flow = mf.flow (s, t); if (flow != sum) { cout << 0 << "\n" ; return 0 ; } cout << 1 << "\n" ; auto edges = mf.edges (); vector<vector<int >> ans (m + 1 ); for (auto [u, v, cap, flow] : edges) { if (1 <= u && u <= m && flow == 1 ) { ans[u].push_back (v - m); } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { for (auto x : ans[i]) { cout << x << " " ; } cout << "\n" ; } return 0 ; }
题意
一张 \(n\) 行 \(m\)
列的方格图,每个方格都有一个正整数,从这张图里面取数,要求任意两个数所在的方格没有公共边,求取出的最大总和。
\(n,m\le 100\)
题解
没学过网络流的可能认为这是一个 dp,可以状压 \(O(n2^m)\)
解决,对于当前数据规模是无法通过的。
如果连边是不相邻的点之间,虽然直观但是复杂度太高了,考虑连不能同时选的边,从总和减去删除的点权。
由于要求相邻格不能同时选,我们可以连边代表这样的限制。不妨对方格图进行黑白染色,每个黑点向周围的白点连边,可以转化为一个二分图模型,要求有连边的两个格子不能同时选。现在我们的问题就转化成了,删去二分图的一些边,要求每条边至少有一个点被删除,且删去的点的权值总和最小。我们新建一个起点
\(s\) 和终点 \(t\) ,从 \(s\) 向黑点连边,容量为点权,从白点向 \(t\)
连边,容量为点权,从黑点向周围的白点连边,容量为
inf。这样,网络的割就代表删去一些边后,不存在 \(s\rightarrow 黑点 \rightarrow 白点 \rightarrow
t\) 的路径,而我们将中间的边容量设置为
inf,因此此时的答案就是所有数的总和减去最小割。
时间复杂度:\(O((nm)^{1.5})\)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; constexpr int inf = 3e18 ;signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector<vector<int >> a (n + 1 , vector <int >(m + 1 )); int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { cin >> a[i][j]; ans += a[i][j]; } } auto id = [&](int x, int y) { return (x - 1 ) * m + y; }; int s = n * m + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MaxFlow<int > mf (t) ; int fx[] = {0 , 0 , 1 , -1 }; int fy[] = {1 , -1 , 0 , 0 }; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { if ((i + j) & 1 ) { mf.addEdge (id (i, j), t, a[i][j]); } else { mf.addEdge (s, id (i, j), a[i][j]); for (int z = 0 ; z < 4 ; z++) { int dx = i + fx[z], dy = j + fy[z]; if (1 <= dx && dx <= n && 1 <= dy && dy <= m) { mf.addEdge (id (i, j), id (dx, dy), inf); } } } } } cout << ans - mf.flow (s, t) << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
\(n\times n\)
的棋盘上,一个马可以攻击他周围的八格(按照象棋规则)。求最多可以放置多少个骑士使得他们彼此互不攻击。同时棋盘上还有
\(m\) 个位置不能放置。
\(n\le 200\)
题解
和上一题类似的思路,黑白染色后会相互攻击的点是不同颜色的,连边即可。
时间复杂度:\(O(N^3)\)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; constexpr int inf = 3e18 ;signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector<vector<int >> vis (n + 1 , vector <int >(n + 1 )); for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; vis[x][y] = true ; } int s = n * n + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MaxFlow<int > mf (t) ; int fx[] = {-2 , -2 , -1 , -1 , 1 , 1 , 2 , 2 }; int fy[] = {-1 , 1 , -2 , 2 , -2 , 2 , -1 , 1 }; auto check = [&](int x, int y) { return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= n && !vis[x][y]; }; auto id = [&](int x, int y) { return (x - 1 ) * n + y; }; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (vis[i][j]) { continue ; } if ((i + j) & 1 ) { mf.addEdge (id (i, j), t, 1 ); } else { mf.addEdge (s, id (i, j), 1 ); for (int z = 0 ; z < 8 ; z++) { int dx = i + fx[z], dy = j + fy[z]; if (!check (dx, dy)) { continue ; } mf.addEdge (id (i, j), id (dx, dy), inf); } } } } cout << n * n - m - mf.flow (s, t) << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
\(n\) 个仓库环形排列,第 \(i\) 个仓库货物为 \(a_i\) ,每次搬运可以将一个货物搬到相邻的仓库中,求最小的搬运量使得库存数量相同。
\(n\le 100,a_i\le 100\) ,保证 \(\sum a_i\) 是 \(n\) 的倍数。
题解
一个经典的最小费用最大流的模型,会了之后可以去做 ABC 421
G 。
每个仓库最终的状态都是平均值,我们将 \(a_i\) 减去平均值,规定一个起点 \(s\) 和终点 \(t\) ,建立如下的模型:
如果 \(a_i\ge 0\) ,从 \(s\) 向 \(i\) 连边,容量为 \(a_i\) ,费用为 0。
如果 \(a_i<0\) ,从 \(i\) 向 \(t\) 连边,容量为 \(-a_i\) ,费用为 0。
将相邻的仓库连边,容量为 inf,费用为 1。
这么连边的道理是,如果 \(a_i\ge
0\) ,说明它可以向其他仓库分配,我们给他同样大小的流量,让它分配到网络中。如果
\(a_i < 0\) ,它需要 \(-a_i\)
的流量,我们将其连向终点,它必须得到这么多流量才能跑满容量。相邻的仓库之间连边,费用为
1 代表一次转移。
这样,跑满最大流说明需要得到流量的点都能被分配到,在此条件下的最小费用就是答案。
时间复杂度:\(O(\sum a_i\times n\log
n)\)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); constexpr int inf = 3e18 ; int n; cin >> n; vector<int > a (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } int sum = accumulate (a.begin () + 1 , a.end (), 0 ) / n; int s = n + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MinCostFlow<int > mf (t) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { a[i] -= sum; } auto nxt = [&](int x) { return x + 1 > n ? 1 : x + 1 ; }; auto lst = [&](int x) { return x - 1 == 0 ? n : x - 1 ; }; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (a[i] >= 0 ) { mf.addEdge (s, i, a[i], 0 ); } else { mf.addEdge (i, t, -a[i], 0 ); } mf.addEdge (i, nxt (i), inf, 1 ); mf.addEdge (i, lst (i), inf, 1 ); } auto [flow, cost] = mf.flow (s, t); cout << cost << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
\(n\) 个工作分配给 \(n\)
个人做,每个工作都要有人做,每个人都要做一件工作。第 \(i\) 个人做第 \(j\) 个工作的效益是 \(c_{i,j}\) 。求所有方案中总效益最小和最大。
\(n\le 50, 0\le c_{i,j}\le 100\)
题解
另一个非常经典的模型,会了之后可以去做
https://qoj.ac/contest/503/problem/1269,注意那题是求 \([1,k]\)
个人做的方案,根据增广路的特性,每找到一条增广路就对应一个答案。
我们新建一个起点 \(s\) 和终点 \(t\) ,将 \(s\) 与工人连边,容量为 1,费用为
0,代表每个工人只能找一个工作做。将工作与 \(t\) 连边,容量为 1,费用为
0,代表每个工作只能一个人做。将工人与工作之间连边,容量为 1,费用为
\(c_{i,j}\) 。
这样跑一次最小费用最大流就是总效益最小了。如果想求最大,将所有费用取相反数,答案的相反数就是最大费用最大流了。
时间复杂度:\(O(nc\times n^2\log
n)\) 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n; cin >> n; int s = 2 * n + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MinCostFlow<int > mf (t) , mf2 (t) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (i, j + n, 1 , w); mf2. addEdge (i, j + n, 1 , -w); } mf.addEdge (s, i, 1 , 0 ); mf2. addEdge (s, i, 1 , 0 ); mf.addEdge (i + n, t, 1 , 0 ); mf2. addEdge (i + n, t, 1 , 0 ); } cout << mf.flow (s, t).second << "\n" ; cout << -mf2.f low(s, t).second << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
\(m\) 个仓库,有 \(a_i\) 个货物,要把所有货物分配到 \(n\) 个商店中,每个商店需要 \(b_i\) 个货物。第 \(i\) 个仓库运输一个单位货物到第 \(j\) 个商店的代价是 \(c_{i,j}\) ,求最小和最大代价。
题解
相信做了上题和分配问题的你已经可以秒了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int m, n; cin >> m >> n; vector<int > a (m + 1 ) , b (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> b[i]; } int s = n + m + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MinCostFlow<int > mf (t) , mf2 (t) ; constexpr int inf = 3e18 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (i, j + m, inf, w); mf2. addEdge (i, j + m, inf, -w); } mf.addEdge (s, i, a[i], 0 ); mf2. addEdge (s, i, a[i], 0 ); } for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { mf.addEdge (j + m, t, b[j], 0 ); mf2. addEdge (j + m, t, b[j], 0 ); } cout << mf.flow (s, t).second << "\n" ; cout << -mf2.f low(s, t).second << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
\(n\) 道题,每道题有不同类别。有
\(k\)
种类别,从题目中选择一些题组成试卷,对于每一类题目的数量都有要求,求方案或判断无解。
题解
可能这种建模你都做烦了,So easy~输出方案枚举边即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int k, n; cin >> k >> n; int s = n + k + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MaxFlow<int > mf (t) ; int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= k; i++) { int w; cin >> w; sum += w; mf.addEdge (i + n, t, w); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int x; cin >> x; for (int j = 1 ; j <= x; j++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (i, w + n, 1 ); } mf.addEdge (s, i, 1 ); } if (mf.flow (s, t) != sum) { cout << "No Solution!\n" ; return 0 ; } vector<vector<int >> ans (k + 1 ); auto edges = mf.edges (); for (auto [u, v, c, f] : edges) { if (1 <= u && u <= n && f == 1 ) { ans[v - n].push_back (u); } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= k; i++) { cout << i << ": " ; for (auto x : ans[i]) { cout << x << " " ; } cout << "\n" ; } return 0 ; }
题意
\(n\)
根柱子,在柱子中放球,编号依次为 1,2,3,...
要求同一根柱子中相邻的球的编号之和必须是某一个平方数。求最多能放多少球,并给出每根柱子的方案数。
\(n\le 55\)
题解
来了点不一样的。有一个性质是:Dinic
算法是可以动态加点的。我们在每次调用 flow(s, t)
是在残余网络上继续增广,而不是从头再来。因此加边后调用
Dinic,得到的是相比于上次增广新得到的流量。
我们考虑对于每个数,从比他小的,并且可以组成平方数的到它连边,容量为
1。考虑到一个数被放到柱子中有两种情况:一种是单独放进一个柱子;一种是与柱子上其他数组合。我们考虑将每个点拆成
\((2i, 2i + 1)\)
两个点,用来表示这两种关系,即 \(s\rightarrow
2i\) 和 \(2i+1\rightarrow
t\) 。每加入一个数,我们再进行连边,跑一次最大流,这样流量为 0
就能表示没有从 \(s\) 出发到达 \(t\) 的路径,需要单开一个柱子。
输出方案数可以遍历所有边,将有流量的边通过一个 \(nxt\) 数组维护,然后输出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n; cin >> n; int s = 500000 , t = 500001 ; MaxFlow<int > mf (t) ; int num = 0 ; int u = 0 ; while (u <= n) { num++; mf.addEdge (s, 2 * num, 1 ); mf.addEdge (2 * num + 1 , t, 1 ); for (int i = sqrt (num) + 1 ; i * i < num * 2 ; i++) { mf.addEdge ((i * i - num) * 2 , 2 * num + 1 , 1 ); } if (mf.flow (s, t) == 0 ) { u++; } } num--; cout << num << "\n" ; vector<int > nxt (num + 1 ) , vis (num + 1 ) ; auto edges = mf.edges (); for (auto [u, v, c, f] : edges) { if (u == s || v == t || f == 0 ) { continue ; } nxt[u / 2 ] = v / 2 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= num; i++) { if (vis[i]) { continue ; } int j = i; while (j) { cout << j << " " ; vis[j] = true ; j = nxt[j]; } cout << "\n" ; } return 0 ; }
题意
给定 \(n\)
个开区间,选择一些区间,使得对于任意位置 \(x\) ,包含 \(x\) 的开区间个数不超过 \(k\) ,求满足条件的方案的长度总和的最大值。
\(n\le 500,k\le 3,l,r\le 10^5\)
题解
考虑如何建立模型。如果对于每一个点 \(x\)
都向包含它的开区间连边,一方面边数可能过多,另一方面如果一个点对应一个区间,不能让这个区间的其他点也被钦定选择。
我们可以发现如果两个区间不相交,它们是可以同时选择的,并不会受到
\(k\)
的限制的影响,不妨考虑下面的模型:对于两个区间 \((l_1,r_1),(l_2,r_2),r_1\le l_2\) ,我们将
\(r_1\) 连向 \(l_2\) ,容量为 1,费用为 \(l
-r\) ,代表同时选择。我们可以再建立三个源点 \(s_1,s_2\) 和 \(t\) ,从 \(s_1\) 向 \(s_2\) 连边,容量是 \(k\) ,费用是 0。再对于所有区间 \((l,r)\) ,将 \(l\) 连向 \(r\) ,容量为 1,费用为 0,将 \(r\) 连向 \(t\) ,容量为 1,费用为 0。
在这样的模型下,我们找到的一条增广路实际上就是选择了一些互不相交的区间,且费用是最小的(相反数是长度最大的)。而我们能进行这样的操作
\(k\)
次,跑一次最小费用最大流即可。
时间复杂度:\(O(n^2)\)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, k; cin >> n >> k; int s1 = 2 * n + 1 , s2 = s1 + 1 , t = s2 + 1 ; MinCostFlow<int > mf (t) ; mf.addEdge (s1, s2, k, 0 ); vector<array<int , 2>> a (n + 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int l, r; cin >> l >> r; a[i] = {l, r}; mf.addEdge (s2, 2 * i - 1 , 1 , 0 ); mf.addEdge (2 * i - 1 , 2 * i, 1 , l - r); mf.addEdge (2 * i, t, 1 , 0 ); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { auto [x, y] = a[i]; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (i == j) { continue ; } auto [p, q] = a[j]; if (x >= q) { mf.addEdge (2 * i, 2 * j - 1 , 1 , 0 ); } } } cout << -mf.flow (s1, t).second << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
给定 \(n\) 条开线段(\(XOY\)
平面上,两端为空心点),选择一些线段,使得对于任意坐标 \(x_0\) ,作直线 \(x
= x_0\) 与选择的线段最多只有 \(k\) 条相交,求选择的线段的最大长度和。
\(n\le 500, k\le 13\) 。
题解
和上一题非常类似,唯一的区别是可能存在两条垂直于 \(x\)
轴的线段,按照上题的建边方式,会认为他们不相交,实际上是会相交的。如果
\(x_1 = x_2\) 我们可以将 \((x_1,x_2)\) 变换为 \((2x_1,2x_2 + 1)\) ,否则变换为 \((2x_1+1,2x_2)\) ,这样就可以避免这种情况,且不会对其他情况产生影响,因为之前的情况下,\((l_1,r_1),(l_2,r_2)\) 。相交的条件是 \(r_1 - l_2 \ge 1\) ,变换后就变成了 \(2r_1 - (2l_2+1) \ge 1\) ,也就是 \(r_1-l_2\ge 1\) 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, k; cin >> n >> k; int s1 = 2 * n + 1 , s2 = s1 + 1 , t = s2 + 1 ; MinCostFlow<int > mf (t) ; mf.addEdge (s1, s2, k, 0 ); vector<array<int , 2>> a (n + 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int l, r; cin >> l >> r; a[i] = {l, r}; mf.addEdge (s2, 2 * i - 1 , 1 , 0 ); mf.addEdge (2 * i - 1 , 2 * i, 1 , l - r); mf.addEdge (2 * i, t, 1 , 0 ); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { auto [x, y] = a[i]; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (i == j) { continue ; } auto [p, q] = a[j]; if (x >= q) { mf.addEdge (2 * i, 2 * j - 1 , 1 , 0 ); } } } cout << -mf.flow (s1, t).second << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
给定 \(m\)
个任务,每个任务需要若干仪器来完成,完成任务后会获得奖金 \(p_j\) ,\(n\) 台仪器的价格是 \(c_i\) ,求选择任务和仪器做实验能获得的最大收益(奖金
- 仪器价格)
\(n,m\le 50,c_i,p_j<2^{31}\)
题解
这是另一个经典的最小割模型——最大权闭合子图。
可能你会想到费用流,但是无法表示可以不选择所有实验,这种题的做法是,先求出所有奖金之和,再新增起点
\(s\) 和终点 \(t\) ,将 \(s\) 连向每个任务,容量为 \(p_j\) ,从每台仪器连向 \(t\) ,容量为 \(c_i\) ,从每个任务连向对应的仪器,容量为
inf。由于中间的点都是
inf,我们跑最小割,割掉的都是两边的边,我们将奖金之和减去最小割,都是最终答案,因为此时的一个割代表我们不选择一些任务,也不选择一些仪器,我们的答案等于
= 所有正权值之和 - 我们未选择的正权值点的权值之和 +
我们选择的负权值点的权值之和,后者两项实际上就是割,减去最小割就是最大答案。
后文还会对最小割模型给出更详细的描述。
时间复杂度:\(O(n^2)\)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () constexpr int inf = 3e18 ; int m, n; cin >> m >> n; int s = m + n + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MaxFlow<int > mf (t) ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (s, i, w); ans += w; char c; int j; while (true ) { cin >> j; c = getchar (); mf.addEdge (i, j + m, inf); if (c == '\r' || c == '\n' ) { break ; } } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (i + m, t, w); } int f = mf.flow (s, t); auto edges = mf.edges (); for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { if (mf.h[i] != -1 ) { cout << i << " " ; } } cout << "\n" ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (mf.h[j + m] != -1 ) { cout << j << " " ; } } cout << "\n" ; cout << ans - f << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
给定一张 DAG,求最小路径覆盖。
\(n\le 150,m\le 5000\)
题解
最小路径覆盖问题是在一张有向图中,选择最少数量的简单路径,使得所有顶点都恰好出现在一条路径中。
注意最小路径覆盖 = 点的数量 -
点之间匹配数,因为每合并两条路径,路径覆盖数就会减少
1。那么我们可以求点之间匹配数的最大值。建立二分图模型,对于每条有向边
\((u, v)\) ,连边 \((u,v^\prime)\) ,跑最大流即可。对于输出答案,可以采用并查集的方式,但是要小心有重边。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MaxFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; _Edge(int to, T cap) : to (to), cap (cap) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<int > cur, h; MaxFlow () {} MaxFlow (int n) { init (n); } void init (int n) this ->n = n; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); cur.resize (n + 1 ); } bool bfs (int s, int t) h.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::queue<int > q; h[s] = 0 ; q.push (s); while (!q.empty ()) { const int u = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto i : g[u]) { auto [v, c] = e[i]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == -1 ) { h[v] = h[u] + 1 ; if (v == t) { return true ; } q.push (v); } } } return false ; } T dfs (int u, int t, T f) { if (u == t) { return f; } auto r = f; for (int &i = cur[u]; i < g[u].size (); i++) { const int j = g[u][i]; auto [v, c] = e[j]; if (c > 0 && h[v] == h[u] + 1 ) { auto a = dfs (v, t, std::min (r, c)); e[j].cap -= a; e[j ^ 1 ].cap += a; r -= a; if (r == 0 ) { return f; } } } return f - r; } void addEdge (int u, int v, T c) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, c); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 ); } T flow (int s, int t) { T ans = 0 ; while (bfs (s, t)) { cur.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); ans += dfs (s, t, std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); } return ans; } std::vector<bool > minCut () { std::vector<bool > c (n + 1 ) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { c[i] = (h[i] != -1 ); } return c; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; struct DSU { int n; std::vector<int > p, sz; DSU (int n_) { n = n_; init (n); } void init (int n) p.resize (n + 1 ); sz.resize (n + 1 , 1 ); iota (p.begin () + 1 , p.end (), 1 ); } int find (int x) while (x != p[x]) { x = p[x] = p[p[x]]; } return x; } bool merge (int x, int y) x = find (x); y = find (y); if (x == y) { return false ; } sz[y] += sz[x]; p[x] = y; return true ; } bool same (int x, int y) return find (x) == find (y); } int size (int x) return sz[find (x)]; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; int s = n + n + 1 , t = s + 1 ; vector<vector<int >> adj (n + 1 ); MaxFlow<int > mf (t) ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { int u, v; cin >> u >> v; mf.addEdge (u, v + n, 1 ); adj[u].push_back (v); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { mf.addEdge (s, i, 1 ); mf.addEdge (i + n, t, 1 ); } int f = mf.flow (s, t); DSU dsu (n) ; auto edges = mf.edges (); for (auto [u, v, c, f] : edges) { if (1 <= u && u <= n && f == 1 ) { dsu.merge (v - n, u); } } auto output = [&](this auto &&output, int x) -> void { cout << x << " " ; for (auto y : adj[x]) { if (dsu.same (x, y)) { output (y); return ; } } }; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (dsu.find (i) == i) { output (i); cout << "\n" ; } } cout << n - f << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
给定一些机器人的出发位置和最终目的地,他们只能向右或向上走,每经过一条边会获得该边对应的权值(但每个格子只能被获得一次),求能获得的权值最大值。
题解
最大费用最大流。直接建立起点 \(s\)
和终点 \(t\) ,\(s\)
向机器人的起点连边,容量为该点出发的机器人数量,费用为 0,机器人的终点向
\(t\)
连边,容量为到达该点的机器人数量,费用为 0。网格图按照边权建边,容量为
1,费用为边权的相反数。但是考虑到某点的权值被拿走后,机器人仍可能会经过这里,因此还要额外连一条容量为
inf,费用为 0 的边。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int a, b; cin >> a >> b; int P, Q; cin >> P >> Q; int s = (P + 1 ) * (Q + 1 ) + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MinCostFlow<int > mf (t) ; auto getid = [&](int x, int y) { return x * (Q + 1 ) + y; }; constexpr int inf = 3e18 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= P; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < Q; j++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (getid (i, j), getid (i, j + 1 ), 1 , -w); mf.addEdge (getid (i, j), getid (i, j + 1 ), inf, 0 ); } } for (int j = 0 ; j <= Q; j++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < P; i++) { int w; cin >> w; mf.addEdge (getid (i, j), getid (i + 1 , j), 1 , -w); mf.addEdge (getid (i, j), getid (i + 1 , j), inf, 0 ); } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= a; i++) { int k, x, y; cin >> k >> x >> y; mf.addEdge (s, getid (x, y), k, 0 ); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= b; i++) { int k, x, y; cin >> k >> x >> y; mf.addEdge (getid (x, y), t, k, 0 ); } cout << -mf.flow (s, t).second << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
题意
给定一个方形网格图,从 \((1, 1)\)
走到 \((n,n)\) 。设立一些加油站,每到达一个加油站,就把油箱加满
\(k\) 容量,花费 \(A\)
元,走一步需要消耗一个单位油量,如果是向下或向左走,还会付 \(B\)
的费用。还可以在任意位置新增加油站,费用为 \(C\) ,求走到终点的最小费用。
题解
考虑到油量的影响,建立分层图解决。主要是注意连边的细节,每一层向下一层的周围一个方向连边,起点只连接第一层的
\((1,1)\) ,终点连接所有层的 \((n,n)\) 。如果一个点是加油站,必须连向第一层的同一位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;using i64 = long long ;using u64 = unsigned long long ;using u32 = unsigned ;using u128 = unsigned __int128;using i128 = __int128;using ld = long double ;template <class T >struct MinCostFlow { struct _Edge { int to; T cap; T cost; _Edge(int to_, T cap_, T cost_) : to (to_), cap (cap_), cost (cost_) {} }; int n; std::vector<_Edge> e; std::vector<std::vector<int >> g; std::vector<T> h, dis; std::vector<int > pre; bool dijkstra (int s, int t) dis.assign (n + 1 , std::numeric_limits<T>::max ()); pre.assign (n + 1 , -1 ); std::priority_queue<std::pair<T, int >, std::vector<std::pair<T, int >>, std::greater<std::pair<T, int >>> pq; dis[s] = 0 ; pq.emplace (0 , s); while (!pq.empty ()) { T d = pq.top ().first; int u = pq.top ().second; pq.pop (); if (dis[u] != d) { continue ; } for (auto i : g[u]) { int v = e[i].to; T cap = e[i].cap; T cost = e[i].cost; if (cap > 0 && dis[v] > d + h[u] - h[v] + cost) { dis[v] = d + h[u] - h[v] + cost; pre[v] = i; pq.emplace (dis[v], v); } } } return dis[t] != std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); } MinCostFlow () {} MinCostFlow (int n_) { init (n_); } void init (int n_) n = n_; e.clear (); g.assign (n + 1 , {}); } void addEdge (int u, int v, T cap, T cost) g[u].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (v, cap, cost); g[v].push_back (e.size ()); e.emplace_back (u, 0 , -cost); } std::pair<T, T> flow (int s, int t) { T flow = 0 ; T cost = 0 ; h.assign (n + 1 , 0 ); while (dijkstra (s, t)) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { h[i] += dis[i]; } T aug = std::numeric_limits<T>::max (); for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { aug = std::min (aug, e[pre[i]].cap); } for (int i = t; i != s; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].to) { e[pre[i]].cap -= aug; e[pre[i] ^ 1 ].cap += aug; } flow += aug; cost += aug * h[t]; } return {flow, cost}; } struct Edge { int from; int to; T cap; T cost; T flow; }; std::vector<Edge> edges () { std::vector<Edge> a; for (int i = 0 ; i < e.size (); i += 2 ) { Edge x; x.from = e[i + 1 ].to; x.to = e[i].to; x.cap = e[i].cap + e[i + 1 ].cap; x.cost = e[i].cost; x.flow = e[i + 1 ].cap; a.push_back (x); } return a; } }; signed main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); int n, k, a, b, c; cin >> n >> k >> a >> b >> c; vector<vector<int >> g (n + 1 , vector <int >(n + 1 )); int s = n * n * (k + 1 ) + 1 , t = s + 1 ; MinCostFlow<int > mf (t) ; auto getid = [&](int x, int y, int d) { return d * n * n + (x - 1 ) * n + y; }; auto add = [&](int x, int y) { for (int d = 0 ; d < k; d++) { if (x + 1 <= n) { mf.addEdge (getid (x, y, d), getid (x + 1 , y, d + 1 ), 1 , 0 ); } if (y + 1 <= n) { mf.addEdge (getid (x, y, d), getid (x, y + 1 , d + 1 ), 1 , 0 ); } if (x - 1 >= 1 ) { mf.addEdge (getid (x, y, d), getid (x - 1 , y, d + 1 ), 1 , b); } if (y - 1 >= 1 ) { mf.addEdge (getid (x, y, d), getid (x, y - 1 , d + 1 ), 1 , b); } } }; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { cin >> g[i][j]; if (g[i][j] == 1 ) { for (int d = 1 ; d <= k; d++) { mf.addEdge (getid (i, j, d), getid (i, j, 0 ), 1 , a); } if (i + 1 <= n) { mf.addEdge (getid (i, j, 0 ), getid (i + 1 , j, 1 ), 1 , 0 ); } if (j + 1 <= n) { mf.addEdge (getid (i, j, 0 ), getid (i, j + 1 , 1 ), 1 , 0 ); } if (i - 1 >= 1 ) { mf.addEdge (getid (i, j, 0 ), getid (i - 1 , j, 1 ), 1 , b); } if (j - 1 >= 1 ) { mf.addEdge (getid (i, j, 0 ), getid (i, j - 1 , 1 ), 1 , b); } } else { add (i, j); mf.addEdge (getid (i, j, k), getid (i, j, 0 ), 1 , a + c); } } } mf.addEdge (s, getid (1 , 1 , 0 ), 1 , 0 ); for (int i = 0 ; i <= k; i++) { mf.addEdge (getid (n, n, i), t, 1 , 0 ); } cout << mf.flow (s, t).second << "\n" ; return 0 ; }
最小割模型总结
二者选其一
\(n\) 个物品和两个集合 \(A,B\) ,如果一个物品没有放入 \(A\) 集合会花费 \(a_i\) ,没有放入 \(B\) 集合会花费 \(b_i\) ,再给出若干条件 \(u,v,w\) ,代表如果 \(u\) 和 \(v\) 同时不在一个集合里,就会花费 \(w\) 。每个物品必须且只能属于一个集合,求最小花费。
做法:设置源点 \(s\) 和汇点 \(t\) ,\(s\)
向物品连 \(a_i\) ,物品向 \(t\) 连 \(b_i\) ,对于限制 \(u,v,w\) ,\(u,v\) 之间连容量为 \(w\) 的双向边。
此时跑一次最小割,此时割的含义就是没有源点到汇点的路径,即每个点都选择了一个集合。如果割开的是
\(s\) 或 \(t\) 与物品之间的边,代表物品不放在 \(A\) 或者 \(B\) 集合,如果割开的是 \(u,v\)
之间的边,代表两个物品不在一个集合。
最大权闭合子图
给定一张有向图,每个点都有一个权值,需要选择一个权值最大的子图,使得子图中每个点的后继都在子图中。
做法:建立源点 \(s\) 和汇点 \(t\) ,若 \(u\) 权值为正,\(s\) 向 \(u\) 连一条有向边,边权为点权;否则 \(u\) 向 \(t\)
连边,边权为点权相反数。原图中的所有边权,容量变为 inf。
此时跑最小割,将所有正权值之和减去最大流即为答案。